Silicon dioxide CAS#7631-86-9
Silicon dioxide, commonly known as silica, is a naturally occurring compound found in quartz and sand. It is a primary component of most rocks and is widely used in various industries due to its high thermal stability, chemical inertness, and optical clarity. In chemical applications, it is valued for its abrasive, refractory, and adsorptive properties, making it essential in products like glass, ceramics, and electronics.
发送询盘
Silicon dioxide CAS#7631-86-9
| Silicon dioxide Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | >1600???C(lit.) |
| Boiling point | >100???C(lit.) |
| density | 2.2-2.6?g/mL?at 25???C |
| vapor pressure | 13.3hPa at 1732?? |
| refractive index | 1.46 |
| Fp | 2230??C |
| storage temp. | 2-8??C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water and in mineral acids except hydrofluoric acid. It dissolves in hot solutions of alkali hydroxides. |
| form | suspension |
| pka | 6.65-9.8[at 20 ??] |
| Specific Gravity | 2.2 |
| color | White to yellow |
| PH | 5-8 (100g/l, H2O, 20??)(slurry) |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Resistivity | 1??10*20 (??/?̦?.cm) |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 6: forms irreversible hydrate |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Crystal Structure | Trigonal |
| Merck | 14,8493 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: IDLH 3000 mg/m3; TWA 6 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7631-86-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Silicon(iv) oxide(7631-86-9) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 68) 1997 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silica (7631-86-9) |
| Safety Information |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38-36/37-22-43-52/53-36/38 |
| Safety Statements | 26-37/39-36-36/37/39-36/37-61 |
| OEB | B |
| OEL | TWA: 6 mg/m3 |
| HS Code | 2811221000 |
| Toxicity | LC inhalation in rat: > 200gm/m3/1H |
| IDLA | 3,000 mg/m3 |
- 2
- 2-diallylpent-4-en-1-amine
- 4
- 95-16-9
- Ammonium sulfamate
- Benzothiazole
- cas:67889-00-3ح2
- cas:83524-75-8 | pigment black 32
- cas:928836-00-4 | 2
- cas:932745-70-5 | 4
- Chemical Minerals
- Coconut diethanolamide
- Daily Chemicals
- discount
- for sale
- General pvc resin
- hexyl D-glucoside
- in stock
- Lauramidopropyl betaine
- LAURIC ACID MONOETHANOLAMIDE
- Petroleum Additives
- Plasticiser
- Ploymers
- price
- PVC
- quotation
- Raw Materal
- Remove term: Petroleum Additives Petroleum Additive
- SODIUM ETHYL 2-SULFOLAURATE
Related Products
Chemical Name: 3-Hydroxybutyric acid
CAS No.: 625-71-8
Molecular Formula: C4H8O3
Molecular Weight: 104.1
Appearance: White powder
Bentonite, sodium-activated, is a type of clay rich in montmorillonite minerals, which undergoes a process to increase its sodium content. This alteration enhances its swelling and adsorptive properties, making it a highly effective thickener and gel-forming agent. Sodium bentonite is widely used in drilling muds, foundry sands, and as a binder in various industrial applications. Its ability to absorb liquids and form stable gels makes it invaluable in cosmetics, agriculture, and as a component in the manufacturing of ceramics and paper products.
Chemical Name: Ashwagandha Extract
Synonyms: Withania somnifera, ext.; Withania Somnefera Extract
CAS: 90147-43-6
Appearance: Brown
Chemical Name: UV-120
Other Name: (2’,4’-Di-tert-butylphenyl 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzoate)
CAS No.: 4221-80-1
Molecular Fomula: C29H42O3
Molecular weight: 438.66
Assay: ≥99%(LC)
Chemical Name: Potassium Castorate
CAS No.: 8013-05-6
Molecular Formula: C57H107K3O12
Molecular Weight: 1101.74718
Appearance: Yellow Liquid
Chemical Name: Dehydrocholic acid
Synonyms: Acide dehydrocholique; Triketocholanic acid
CAS No.: 81-23-2
Molecular Formula: C24H34O5
Molecular Weight: 402.53
Appearance: Powder
Chemical Name: 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
Other Name: Tetrachlorethane
CAS No.: 79-34-5
Molecular Formula: C2H2Cl4
Molecular Weight: 167.85
Appearance: Liquid
Aluminum chlorohydrate is an inorganic compound often used as a coagulant in water treatment processes. It is also known for its astringent properties and is utilized in various personal care products, such as antiperspirants and deodorants, due to its ability to temporarily close sweat glands. It enhances the viscosity and stability of formulations, making it a valuable ingredient in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Chemical Name: Zinc citrate
Synonyms: Zinc citrate trihydrate
CAS No.: 546-46-3
Molecular Formula: C6H8O7Zn
Molecular Weight: 257.5
Appearance: White powder
Chemical Name: Ammonium Iron(II) Sulfate
Synonyms: Diammonium iron bis(sulphate); iron (ii) ammonium sulfate
CAS No.: 10045-89-3
Molecular Formula: FeH5NO4S
Molecular Weight: 170.95
Chemical Name: STODDARD SOLVENT
CAS No.: 64742-88-7
Appearance: Colorless or Light Yellow Liquid
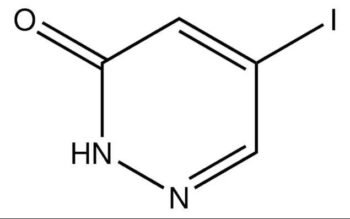
Common English name: 5-iodo-2,3-dihydropyridazin-3-one
CAS No.: 825633-94-1
Molecular formula: C4H3IN2O
Molecular weight: 221.98
Sample: Available