trimebutine maleate cas 34140-59-5
Chemical Name:Trimebutine maleate
CAS: 34140-59-5
Molecular Fomula:C26H33NO9
Molecular Weight:503.54
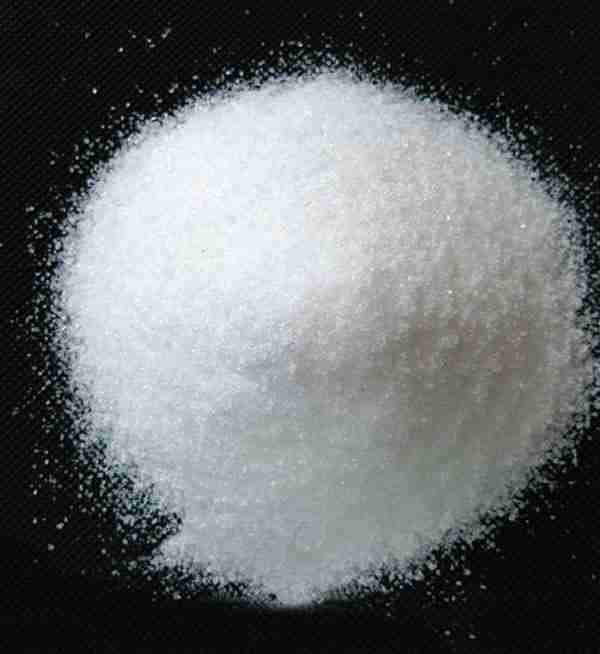
Appearance: White Crystalline Powder
Purity: 99%
发送询盘
Description
Trimebutine maleateQuick Details
Chemical Name:Trimebutine maleate
CAS: 34140-59-5
Molecular Fomula:C26H33NO9
Molecular Weight:503.54
Chemical Structure:
Appearance: White Crystalline Powder
Purity: 99%
Trimebutine maleateTypical Properties
Item
Specification
Product Name
Trimebutine maleate
CAS No.
34140-59-5
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Assay
98.5%-101.5%
Loss on drying
0.5% max
Heavy metals
20ppm max
Total impurity
1.0% max
Trimebutine maleate Usage
Trimebutine maleate has a dual regulatory function on the gastrointestinal tract, regardless of diarrhea or constipation. The pharmacological action is different from the anti-cholinergic and anti-dopamine drug type gastrointestinal motility regulators.
Trimebutine maleate
25 kg/drum
| 5 |
|
0 |
| 4 |
|
0 |
| 3 |
|
0 |
| 2 |
|
0 |
| 1 |
|
0 |
- 2
- 2-diallylpent-4-en-1-amine
- 4
- 95-16-9
- Ammonium sulfamate
- Benzothiazole
- cas:67889-00-3ح2
- cas:83524-75-8 | pigment black 32
- cas:928836-00-4 | 2
- cas:932745-70-5 | 4
- Chemical Minerals
- Coconut diethanolamide
- Daily Chemicals
- discount
- for sale
- General pvc resin
- hexyl D-glucoside
- in stock
- Lauramidopropyl betaine
- LAURIC ACID MONOETHANOLAMIDE
- Petroleum Additives
- Plasticiser
- Ploymers
- price
- PVC
- quotation
- Raw Materal
- Remove term: Petroleum Additives Petroleum Additive
- SODIUM ETHYL 2-SULFOLAURATE
Related Products
Chemical Name: Zinc citrate
Synonyms: Zinc citrate trihydrate
CAS No.: 546-46-3
Molecular Formula: C6H8O7Zn
Molecular Weight: 257.5
Appearance: White powder
Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA or 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine, is a naturally occurring amino acid and a critical precursor in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. With the molecular formula C9H11NO4, levodopa is a large, neutral amino acid that plays a significant role in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and be converted into dopamine.
Chemically, levodopa is synthesized from the precursor amino acid tyrosine through the action of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. As a medication, levodopa is often formulated with a peripheral DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor to reduce its conversion to dopamine outside the brain, thereby increasing its effectiveness and reducing side effects.
Levodopa is characterized by its effectiveness in alleviating the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. It is typically administered orally and absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, where it is then transported to the brain.
In summary, levodopa is a vital pharmaceutical compound used in neurology for its role in treating Parkinson’s disease by replenishing the brain’s dopamine levels. Its targeted delivery and conversion to dopamine make it an essential treatment option for managing the motor symptoms associated with this condition.
Chemical Name: Choline salicylate
CAS No.: 2016-36-6
Molecular Formula: C12H19NO4
Molecular Weight: 241.28
Appearance: Red-Brown Crystal
Chemical Name:?Tebipenem pivoxil
CAS No.: 161715-24-8
Molecular Formula: C22H31N3O6S2
Molecular Weight: 497.63
Product name:Cyclopentane
Purity:96%
Appearance:White powder
Package:25kg/bag
Sample:Available
Chemical Name:?Favipiravir
CAS No.:?259793-96-9
Molecular Fomula:?C5H4FN3O2
Molecular weight:?157.1
Appearance:?Off white solid
Assay: 99 % min
Lidocaine hydrochloride is an anesthetic as well as an antiarrhythmic drug. Clinically, it is mainly used for infiltration anesthetic, epidural anesthetic, topical anesthesia (consisting of mucosal anesthetic throughout thoracoscopic examination or abdominal surgical treatment) as well as nerve conduction block. It can additionally be used for early ventricular tightenings and also ventricular tachycardia after acute myocardial infarction, and also for ventricular arrhythmias triggered by digitalis poisoning, cardiac surgery as well as cardiac catheterization. But it is usually inadequate for supraventricular arrhythmias.
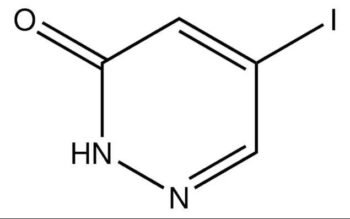
Common English name: 5-iodo-2,3-dihydropyridazin-3-one
CAS No.: 825633-94-1
Molecular formula: C4H3IN2O
Molecular weight: 221.98
Sample: Available
Chemical Name: Sultamicillin
CAS No.: 76497-13-7
Appearance:?White powder
Assay??99.0%
Chemical Name: Arabic gum
CAS No.: 9000-01-5
Appearance: powder
Chemical Name: Ashwagandha Extract
Synonyms: Withania somnifera, ext.; Withania Somnefera Extract
CAS: 90147-43-6
Appearance: Brown
Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA or 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine, is a naturally occurring amino acid and a critical precursor in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. With the molecular formula C9H11NO4, levodopa is a large, neutral amino acid that plays a significant role in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and be converted into dopamine.
Chemically, levodopa is synthesized from the precursor amino acid tyrosine through the action of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. As a medication, levodopa is often formulated with a peripheral DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor to reduce its conversion to dopamine outside the brain, thereby increasing its effectiveness and reducing side effects.
Levodopa is characterized by its effectiveness in alleviating the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. It is typically administered orally and absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, where it is then transported to the brain.
In summary, levodopa is a vital pharmaceutical compound used in neurology for its role in treating Parkinson’s disease by replenishing the brain’s dopamine levels. Its targeted delivery and conversion to dopamine make it an essential treatment option for managing the motor symptoms associated with this condition.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.