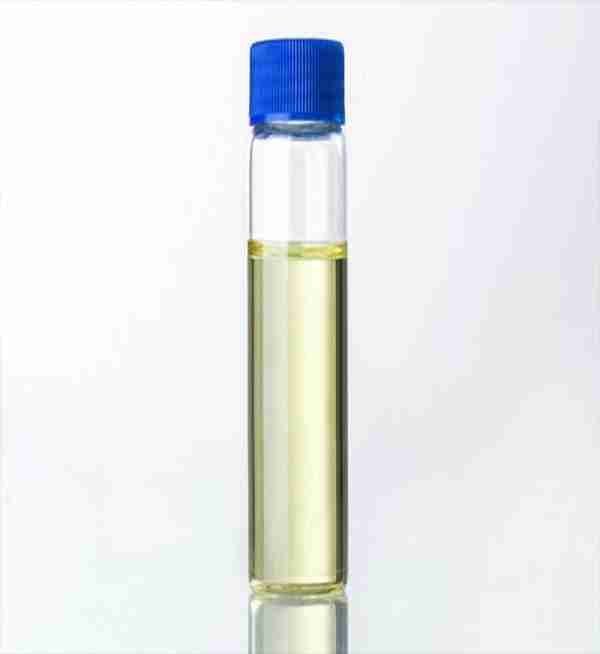
N,N-Dimethylaniline CAS#121-69-7
N,N-Dimethylaniline is an organic compound with amine and methyl groups attached to a benzene ring. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic amine odor. This compound is primarily used as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of dyes, pigments, and polymers. Its reactivity makes it a valuable building block in the production of various organic compounds, particularly in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
发送询盘
N,N-Dimethylaniline CAS#121-69-7
| N,N-Dimethylaniline Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 1.5-2.5 ??C (lit.) |
| Boiling point | 193-194 ??C (lit.) |
| density | 0.956 g/mL at 25 ??C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 2 mm Hg ( 25 ??C) |
| refractive index | n20/D?1.557(lit.) |
| Fp | 158???F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30??C. |
| solubility | 1.2g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 5.15(at 25??) |
| color | Clear yellow |
| Relative polarity | 0.179 |
| PH | 7.4 (1.2g/l, H2O, 20??) |
| explosive limit | 1.2-7%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 1 g/L (20 oC) |
| Merck | 14,3234 |
| BRN | 507140 |
| Henry’s Law Constant | 4.98(x 10-6?atm?m3/mol) at 20 ??C (approximate – calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 5 ppm (25 mg/m3), STEL 10 ppm (50 mg/m3), IDLH 100 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 5 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 ppm, STEL 10 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.4000000000000004 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates, halogens. Combustible. |
| InChIKey | JLTDJTHDQAWBAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 1.171 at 35?? |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 121-69-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenamine, N,N-dimethyl-(121-69-7) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 57) 1993 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N,N-Dimethylaniline (121-69-7) |
- 2
- 2-diallylpent-4-en-1-amine
- 4
- 95-16-9
- Ammonium sulfamate
- Benzothiazole
- cas:67889-00-3ح2
- cas:83524-75-8 | pigment black 32
- cas:928836-00-4 | 2
- cas:932745-70-5 | 4
- Chemical Minerals
- Coconut diethanolamide
- Daily Chemicals
- discount
- for sale
- General pvc resin
- hexyl D-glucoside
- in stock
- Lauramidopropyl betaine
- LAURIC ACID MONOETHANOLAMIDE
- Petroleum Additives
- Plasticiser
- Ploymers
- price
- PVC
- quotation
- Raw Materal
- Remove term: Petroleum Additives Petroleum Additive
- SODIUM ETHYL 2-SULFOLAURATE
Related Products
Chemical Name: Ashwagandha Extract
Synonyms: Withania somnifera, ext.; Withania Somnefera Extract
CAS: 90147-43-6
Appearance: Brown
Product name:HYDROXYPROPYL GUAR HYDROXYPROPYLTRIMONIUM CHLORIDE
Purity:99%
Appearance:Light Yellow Powder
Package:Customized according to customer needs.
Sample:Available
Benzothiazoles are a class of chemical compounds characterized by a fused benzene and thiazole ring. They exhibit a broad spectrum of applications, particularly as antioxidants in rubber and plastic industries, enhancing product longevity and performance. Additionally, benzothiazoles serve as key intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, contributing to the development of life-saving drugs. Recognized for their stability and reactivity, these compounds are integral to advancing material science and healthcare solutions.
Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) is a synthetic phenolic antioxidant commonly added to foods, cosmetics, and packaging to prevent the oxidation of fats and oils, thereby extending their shelf life. It is also used as a preservative in a variety of products, including rubber, petroleum products, and animal feed. BHT is recognized for its effectiveness in maintaining nutrient levels, color, flavor, and odor in food products . It is known to have a melting point of 69-71??C, a boiling point of 265??C, and is soluble in ethanol, acetone, and benzene, but not in water, glycerin, or propylene glycol . BHT is also used in some dietary supplements due to its antioxidant properties . However, it is important to handle BHT with care, as it can cause skin irritation and is considered harmful if swallowed .
Chemical Name: Quercetin-3-O-sophoroside
CAS No.: 18609-17-1
Molecular Formula: C27H30O17
Molecular Weight: 626.52
Silicones are a family of synthetic polymers known for their versatility and stability. They are heat-resistant, non-toxic, and have excellent electrical insulation properties. Commonly used in various industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and personal care products, silicones offer a wide range of applications from sealants and adhesives to lubricants and medical devices. Their resistance to extreme temperatures and weathering makes them a preferred choice for many high-performance applications.
Chemical Name: Zinc citrate
Synonyms: Zinc citrate trihydrate
CAS No.: 546-46-3
Molecular Formula: C6H8O7Zn
Molecular Weight: 257.5
Appearance: White powder
Chemical Name: 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
Other Name: Tetrachlorethane
CAS No.: 79-34-5
Molecular Formula: C2H2Cl4
Molecular Weight: 167.85
Appearance: Liquid
Chemical Name: 3-Hydroxybutyric acid
CAS No.: 625-71-8
Molecular Formula: C4H8O3
Molecular Weight: 104.1
Appearance: White powder
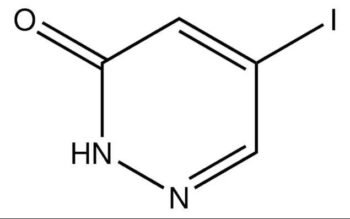
Common English name: 5-iodo-2,3-dihydropyridazin-3-one
CAS No.: 825633-94-1
Molecular formula: C4H3IN2O
Molecular weight: 221.98
Sample: Available
Chemical Name: Dehydrocholic acid
Synonyms: Acide dehydrocholique; Triketocholanic acid
CAS No.: 81-23-2
Molecular Formula: C24H34O5
Molecular Weight: 402.53
Appearance: Powder
Chemical Name: o-Xylene
Synonyms: 1,2-Dimethylbenzene; ortho-xylene
CAS No.: 95-47-6
Molecular Formula: C8H10
Molecular Weight: 106.17